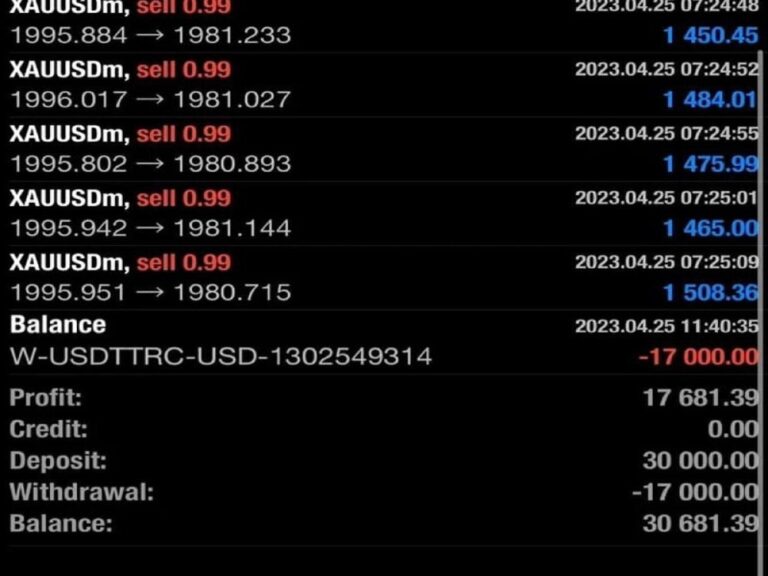
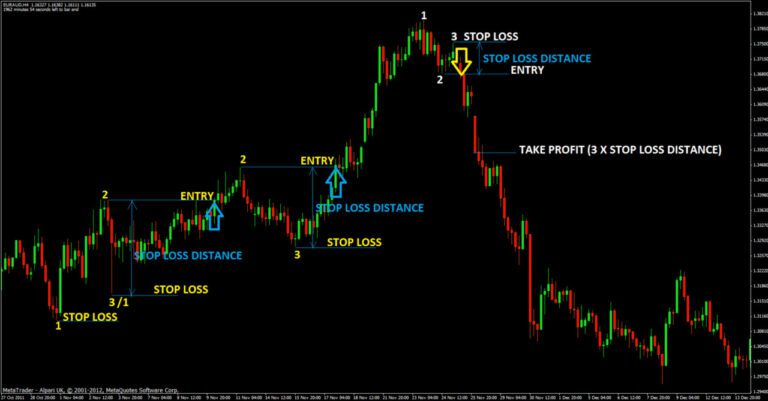
Forex, short for “foreign exchange,” refers to the global marketplace where currencies are traded. Here are the key aspects of forex:
1. Definition
Forex trading involves the buying and selling of currencies in pairs. For example, if you buy the EUR/USD pair, you are buying euros and simultaneously selling US dollars. The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, making it one of the most liquid financial markets in the world.
2. How Forex Works
- Currency Pairs: Currencies are traded in pairs, such as EUR/USD (euro vs. US dollar) or GBP/JPY (British pound vs. Japanese yen). The first currency in the pair is the base currency, and the second is the quote currency.
- Exchange Rate: The exchange rate indicates how much of the quote currency is needed to buy one unit of the base currency. For example, if the EUR/USD exchange rate is 1.20, it means 1 euro is equal to 1.20 US dollars.
- Bid and Ask Price: In forex trading, the bid price is the price at which you can sell the base currency, while the ask price is the price at which you can buy it. The difference between the two is known as the spread.
3. Market Participants
Various participants engage in the forex market, including:
- Banks and Financial Institutions: Major players that conduct large transactions and facilitate trading for clients.
- Corporations: Businesses that engage in forex to hedge against currency fluctuations or facilitate international trade.
- Retail Traders: Individual traders who buy and sell currencies, often using online trading platforms.
- Governments and Central Banks: Entities that intervene in the forex market to stabilize or influence their national currency.
4. Trading Styles
There are various trading styles in forex, including:
- Day Trading: Buying and selling currencies within the same trading day.
- Swing Trading: Holding positions for several days to take advantage of price swings.
- Scalping: Making multiple trades throughout the day to capture small price movements.
5. Factors Influencing Forex Prices
Several factors can impact currency prices, including:
- Economic Indicators: Data such as GDP growth, employment figures, and inflation rates can affect a currency’s value.
- Interest Rates: Central banks set interest rates, and changes can lead to currency appreciation or depreciation.
- Geopolitical Events: Political stability, trade agreements, and international conflicts can influence currency markets.
- Market Sentiment: Traders’ perceptions and reactions to news and events can also drive currency price movements.
6. Advantages of Forex Trading
- High Liquidity: The forex market is highly liquid, meaning trades can be executed quickly and with minimal price changes.
- Leverage: Many brokers offer leverage, allowing traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital.
- Accessibility: Forex trading can be done online, making it accessible to anyone with an internet connection.
Conclusion
Forex is a dynamic and complex market that offers opportunities for traders to profit from currency fluctuations. Understanding the fundamentals of forex trading, including how it works, the participants involved, and the factors influencing currency prices, is essential for anyone looking to trade in this market.